User agents and accessibility
A user agent is any software that retrieves and presents Web content for end users or is implemented using Web technologies. User agents include Web browsers, media players, and plug-ins that help in retrieving, rendering and interacting with Web content. The family of user agents also includes operating system shells, consumer electronics with Web-widgets, and stand-alone applications or embedded applications whose user interface is implemented as a combination of Web technologies.
Read further User Agent Accessibility Guidelines (UAAG) 2.0
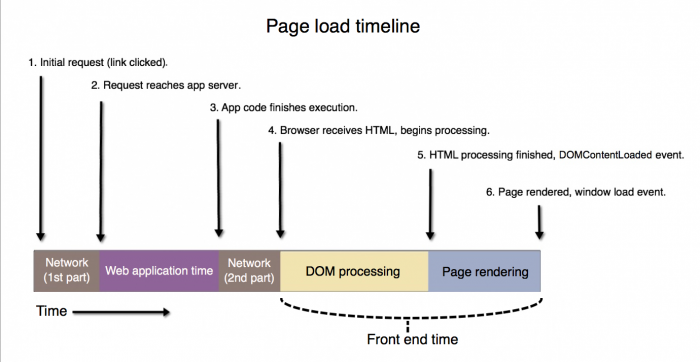
A web browser is an application software used to access the web. Web browsers understand HTML, CSS, and Javascript and render the web pages to the visitors. Web browsers, such as Netscape, Opera, and IE contact remote web servers and make requests on behalf of users. The documents can contain hyperlink points (links) to other documents, which may or may not live on the server that the user originally contacted. Once the browser receives response to its request, it processes the code as depicted in the following diagram:

Guideline 1.1 - Provide access to alternative content. https://www.w3.org/WAI/UA/work/wiki/Browser_Compliance_Notes https://www.w3.org/WAI/UA/2012/ED-UAAG20-20120119/
Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is the process of making a website more visible in search results. Search engines crawl the web, following links from page to page, and index the content found. Crawlers follow rules. If you follow those rules closely, you give the site the best chances of showing up among the first results, increasing traffic.
A web browser is not the same thing as a search engine. A search engine is a website running software that searches data for specified information, then provides links to relevant websites.
Read further The basics of how Search works